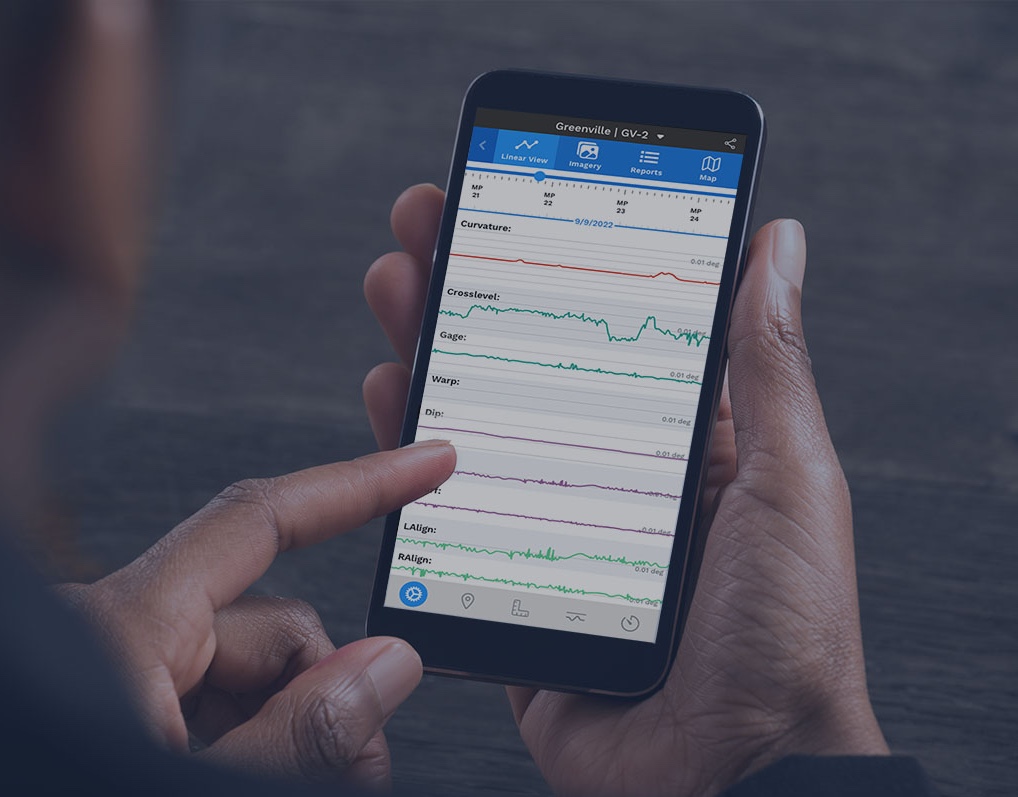
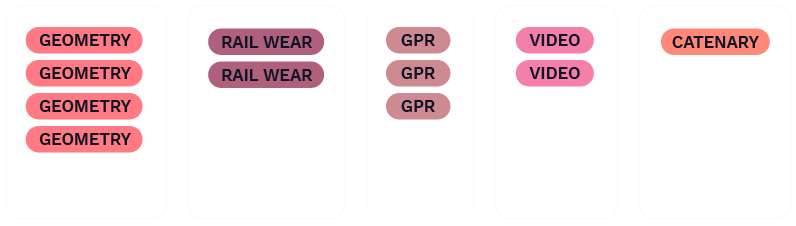
Rail profiles, track geometry, forward-facing video, tie inspections—you name it. As the number of sensors and formats increases, so does the need for tight structure and organization.
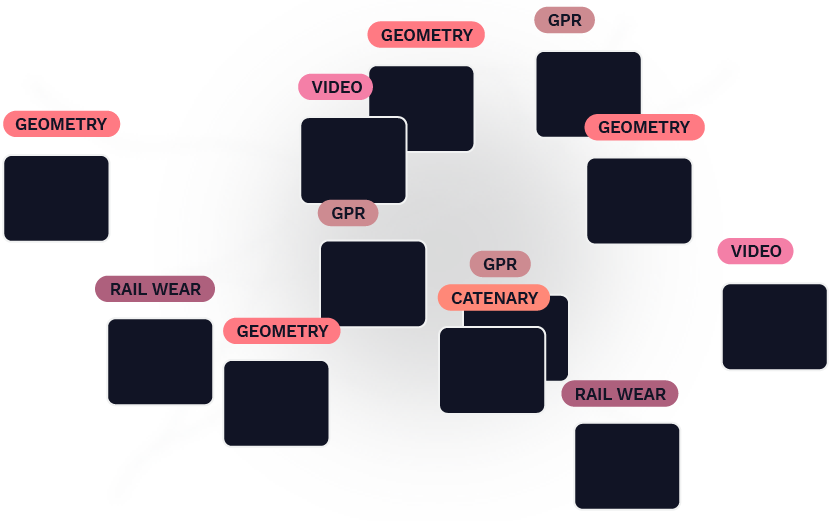
Our process begins with this wide variety of data formats and organizes them into a single data architecture. In essence, this allows various data types to “talk” to each other, rather than being assessed individually.
As part of the uploading process, plugin workflows automatically cleanse and sort data, label attributes, and detect changes. These workflows can be mixed and matched based on particular business needs or goals. For example, a plugin could be added to deal with particularly bad data or integrate weather-related information from an additional sensor.
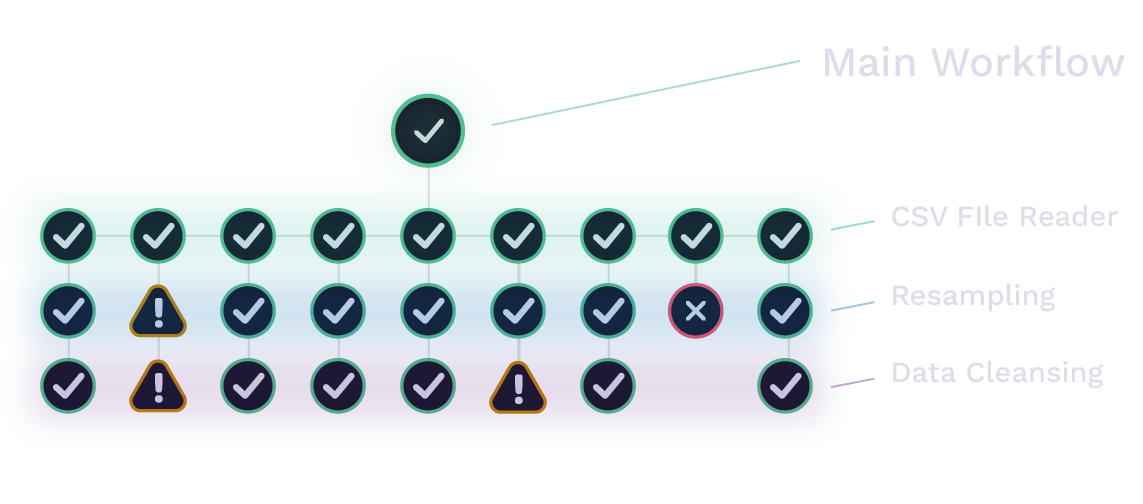
Plugins can be run on-demand, on a timed schedule, or triggered on a data ingestion event. Custom data formats can be handled with specialized plugins that allow nonstandard data to integrate with the rest of the system.
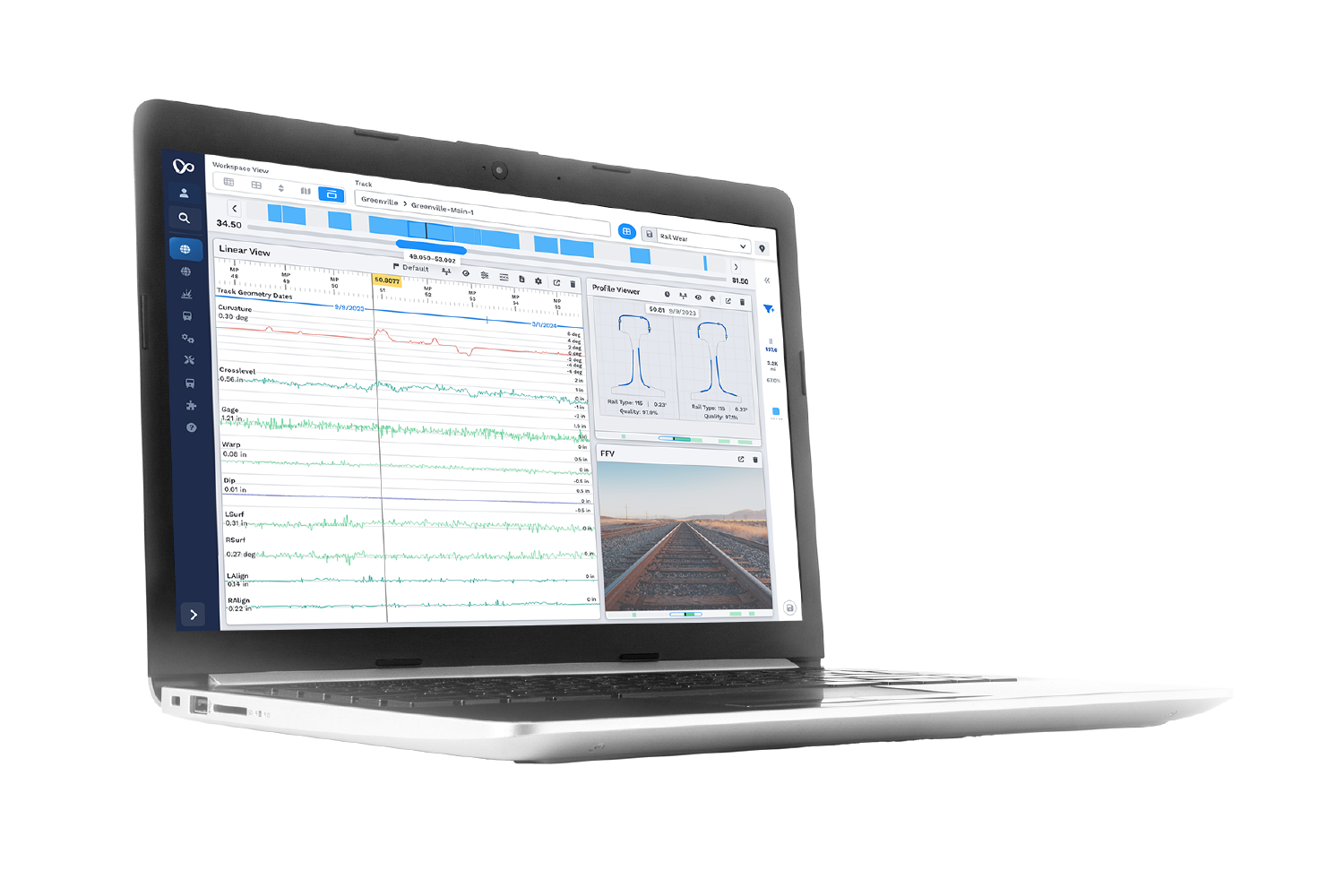
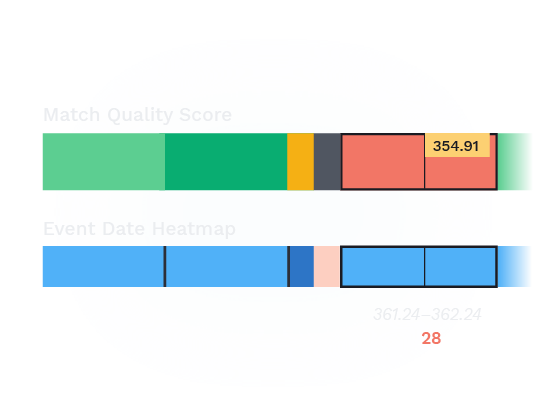
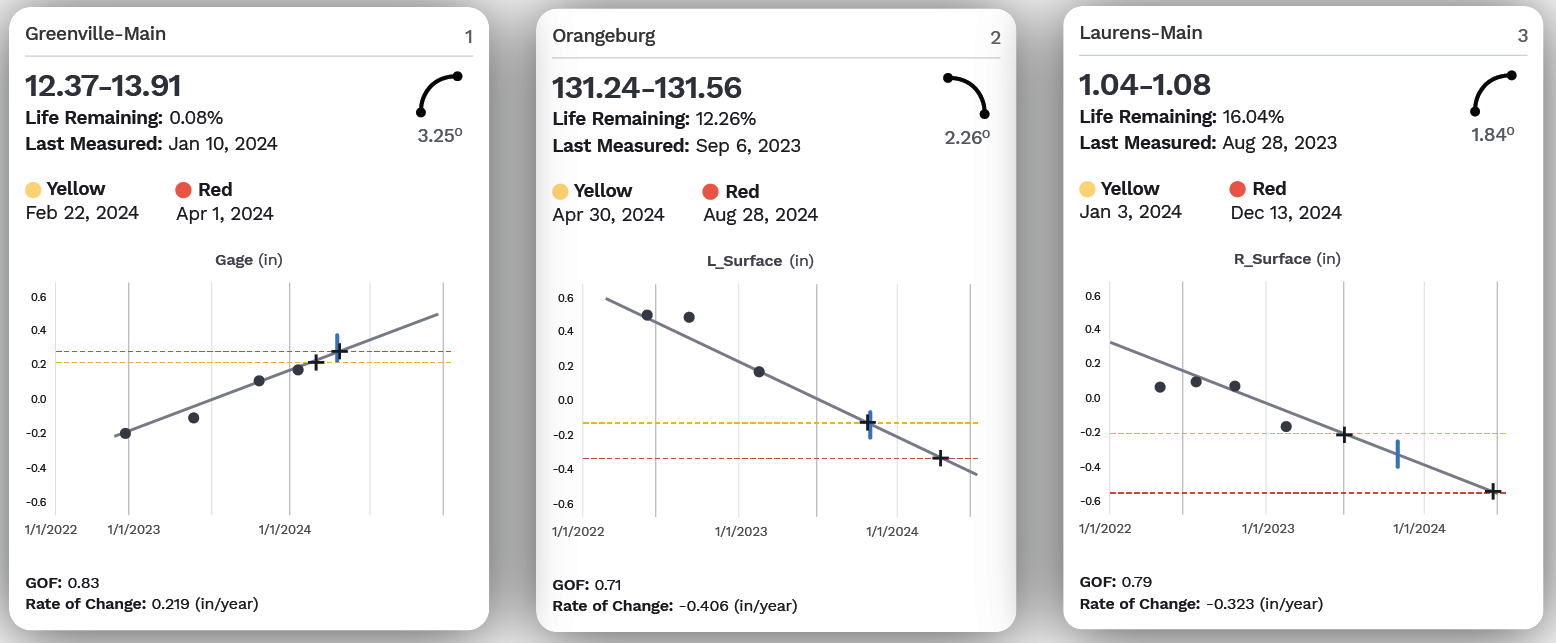
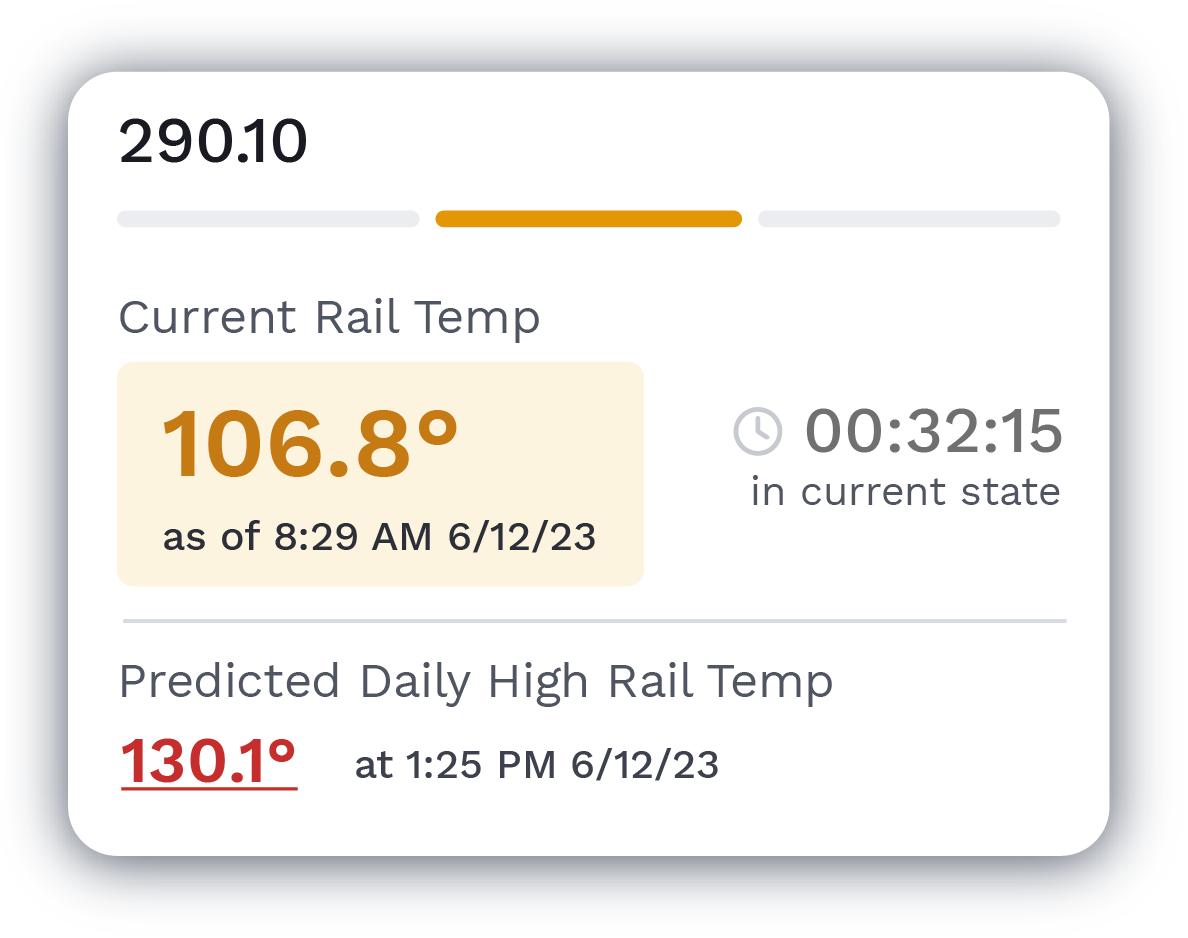
After the new data is fully processed, high-power analytics compare historical trends and visualize trendlines to identify the most urgent areas for maintenance. These visualizations are sent to Global Search and the RailLinks® Workspace, where they can be viewed alongside linear data channels and other data streams.
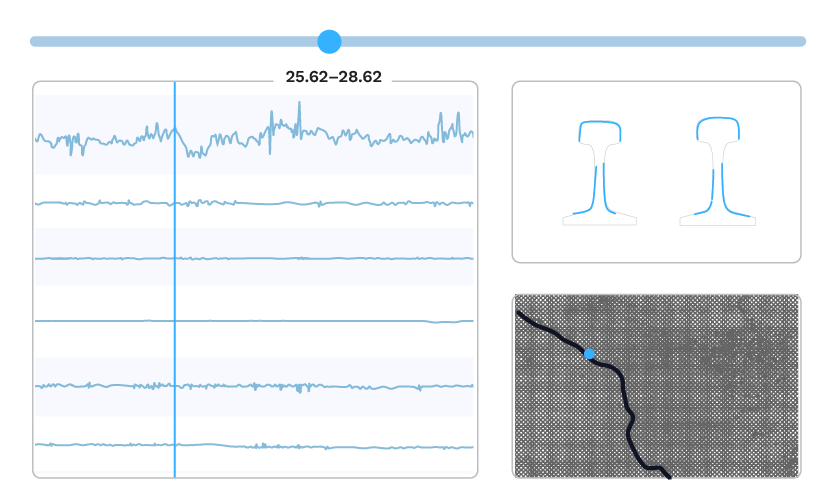
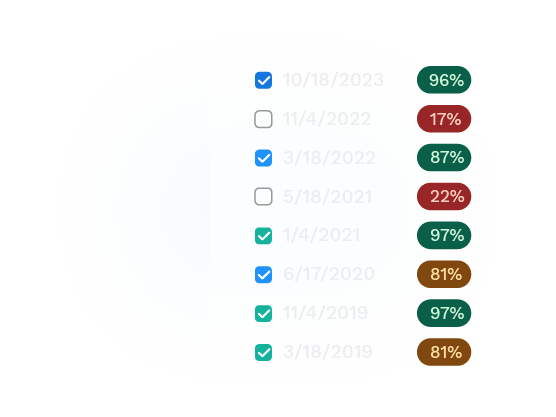
In Global Search, users can view and filter their processed data from across the entire network. Data which crosses critical thresholds can also be sent directly to maintenance personnel through notifications.